A root cause analysis diagram which is also known as a fishbone diagram, Ishikawa diagram, or cause and effect diagram is a graphical representation of all the root causes behind a problem in a business. Companies and organizations use this diagram to find out the real causes behind a problem and to eliminate the problem in the long term. When there is a problem in a business, it is possible that this can be removed for a short period on a sudden basis but that doesn’t mean that this problem won’t arise again in the system. The root cause analysis diagram is a way to make sure that the problem is removed from the roots so that it doesn’t occur again for a long period.
Importance of Root Cause Analysis Diagram:
- It gives the relationship between the causes and the problem:
The best thing about the root cause analysis diagram is that it gives the real-time relationship between the key problem and all the causes behind that issue. This way it is easy for the team members to find a good solution to remove the causes behind the problem so that the problem doesn’t come on the surface again. - It shows all the causes at the same time:
Another key benefit of a root cause analysis diagram is that, unlike many other techniques and strategies for finding causes behind problems, it provides all the causes at the same time which means it is convenient for the team members to find the solutions at the same time without missing anything. When there is more than one cause behind a problem, someone may miss at least a little bit of detail which can cause another issue in the future. With all the causes in front at the same time, the team can eliminate them at the same time too. - It helps to brainstorm:
It is not very easy to find a solution to remove a problem from the system and with root cause analysis diagram, helps the team members to think outside the box and come up with solutions that otherwise seem irrelevant or useless. Brainstorming is something that every business needs and a root cause analysis diagram helps businesses to find better ways for brainstorming. - It helps to keep and maintain team focus on the problems:
With a root cause analysis diagram, it is easy for the team to keep their focus on the problems all the time. When there is more than one cause behind a problem, everyone thinks that he is missing something which can distract his attention from the key steps and elements. This diagram makes sure that no one misses anything and that the solution to the problem is long-term.
Free Root Cause Analysis Diagram:
As we have discussed above a root cause analysis diagram is used for finding out the causes behind problems in a business, that makes it clear that this technique is used in companies and organizations to find problems and not only problems but their causes and the solutions for removing the key causes behind issues and obstacles.
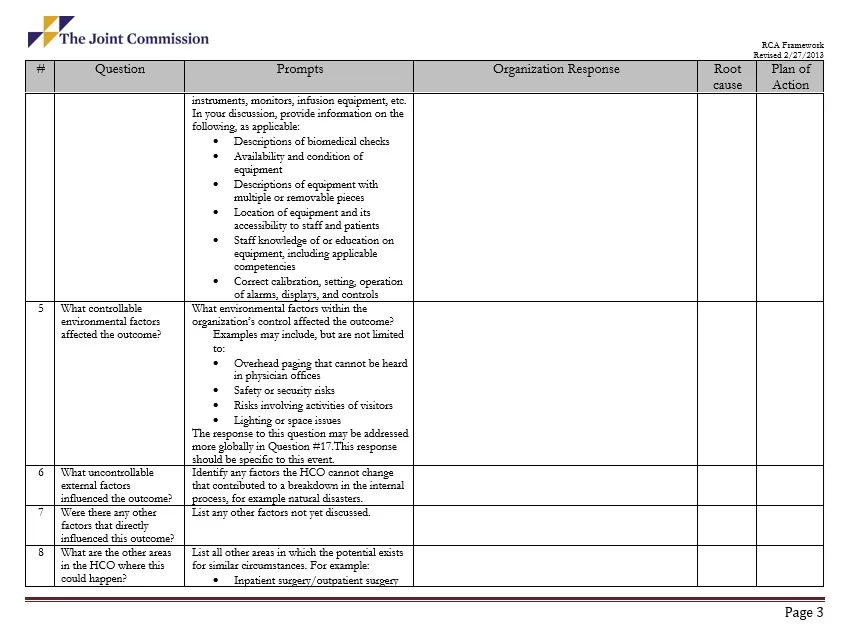
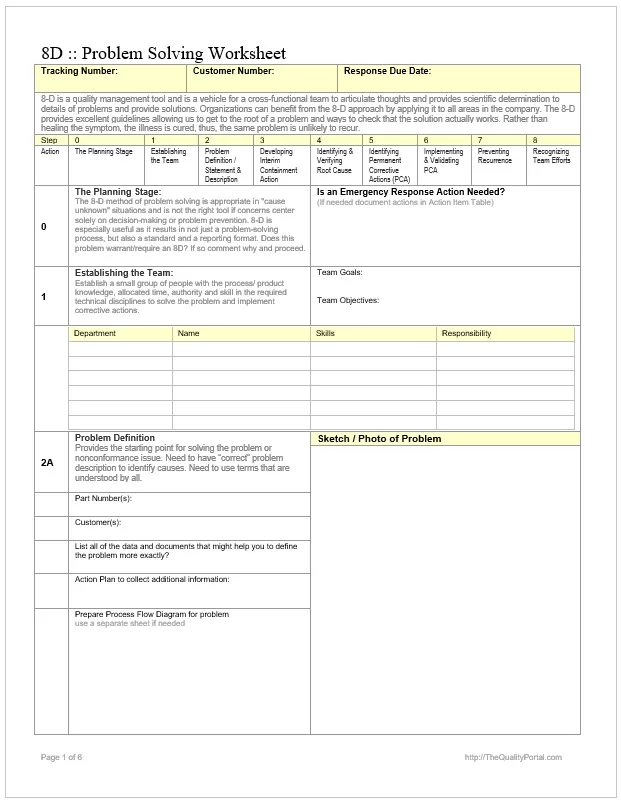
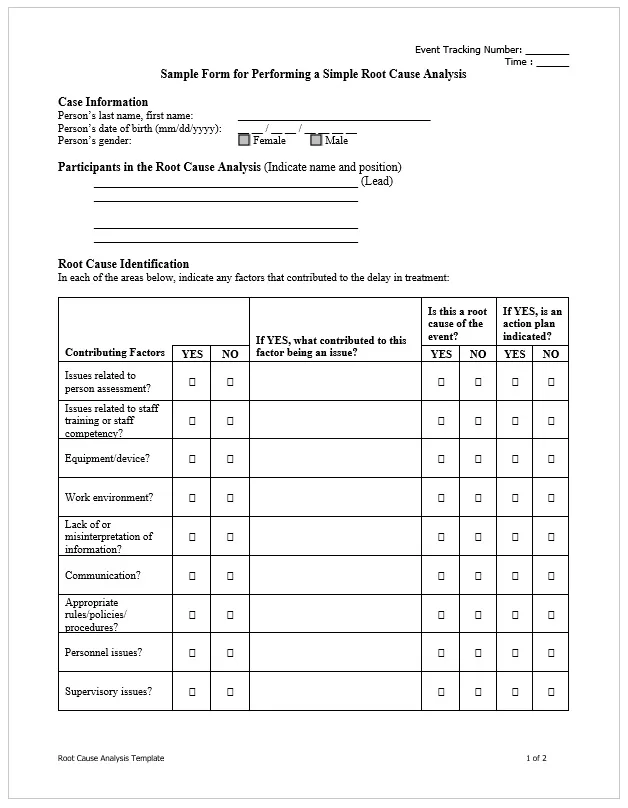
Here is a preview of a Free Sample Root Cause Analysis Diagram Template created using MS Word,
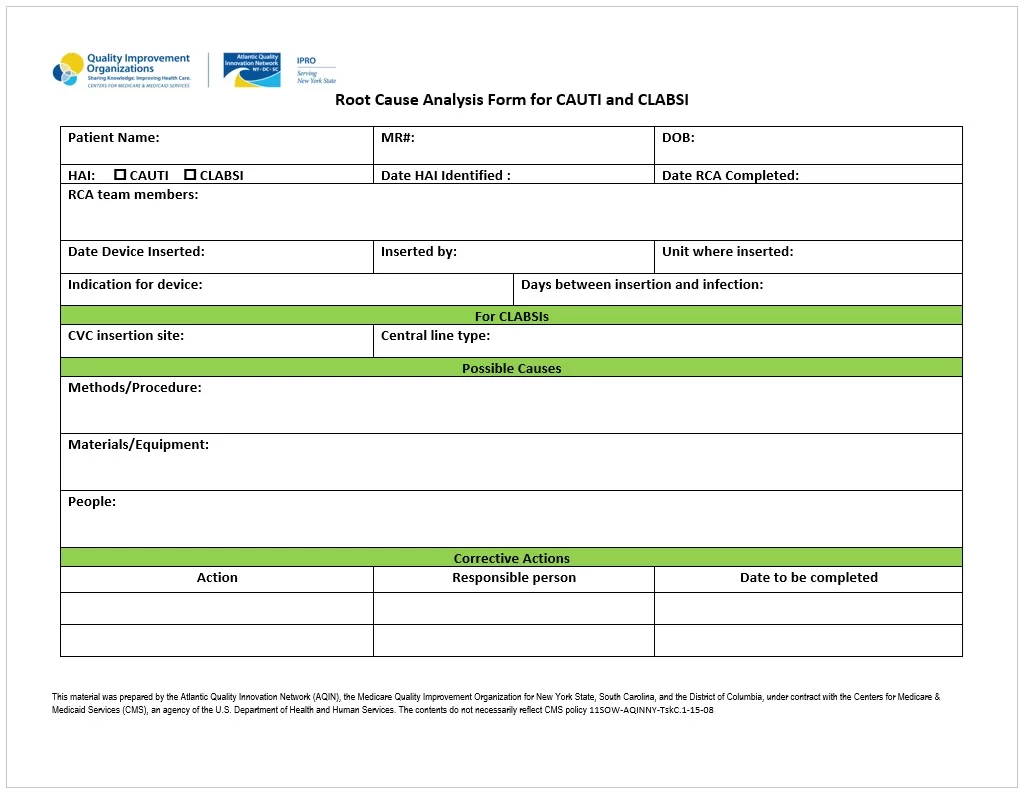

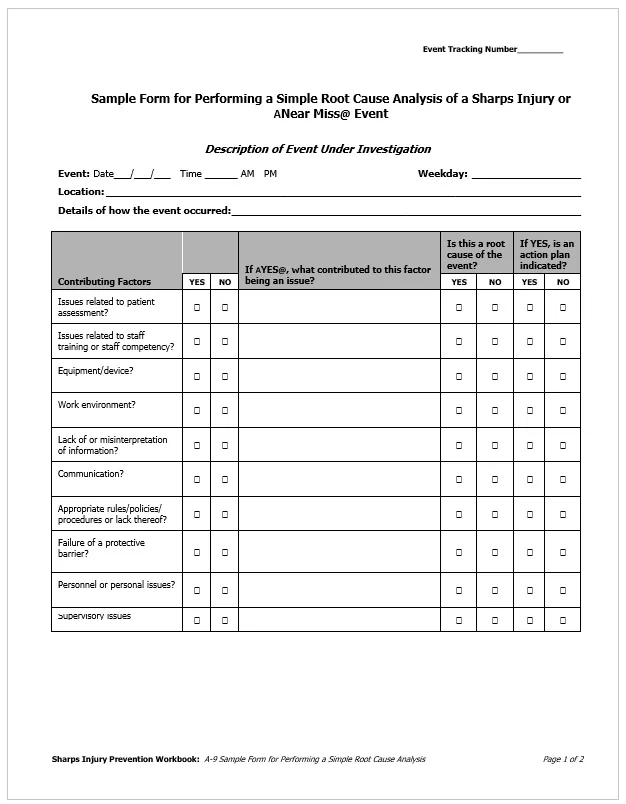
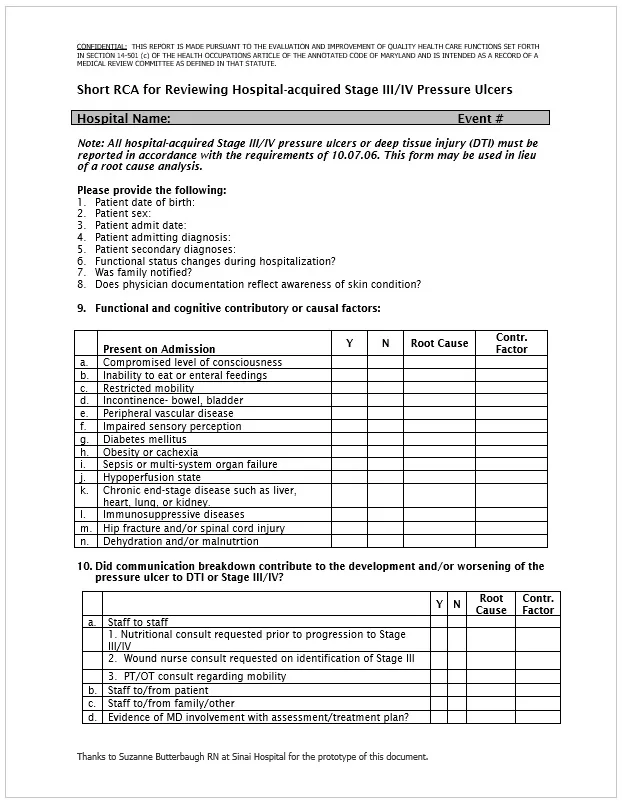
Types of Root Cause Analysis
Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram
The RCA Fishbone Diagram, or the Ishikawa Fishbone diagram, is among the most prevalent root cause analysis tools. The method provides a framework for team members to investigate the possible sources of an issue in a graphical way, categorizing the activities under certain groups which may include people, processes, materials, environment, and many others. This helps to analyze reasons for problems in well-organized fashion which makes it possible to scrutinize each and every reason for such problems. Fishbone diagrams find application particularly in manufacturing, healthcare and service sectors as multiple reasons can cause any given problem. Using this RCA method key areas that need improvement can be determined to come up with practical measures.
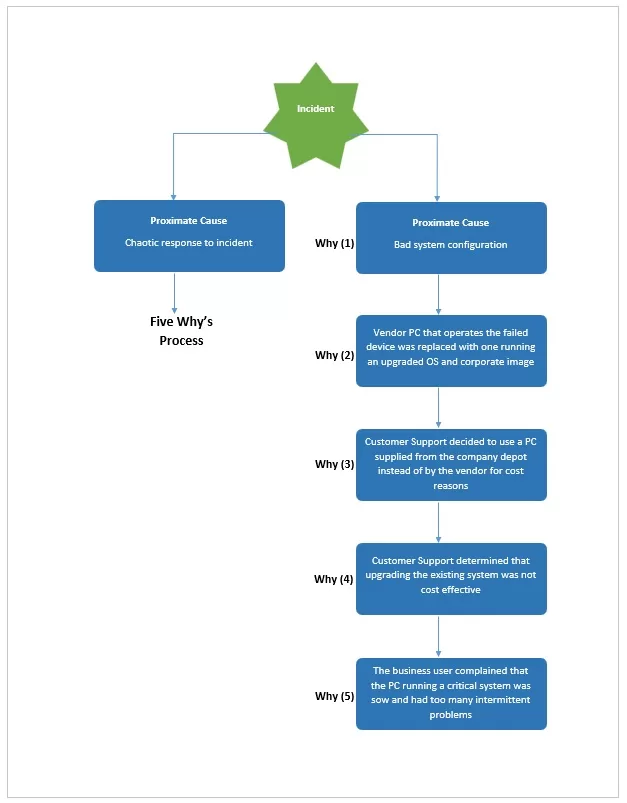
5 Whys Analysis
The RCA method based on the 5 Whys is a very easy-to-use and efficient tool for root cause analysis in which a question “why” is being repeated until the root of a given issue or situation is discovered. This works effectively, especially whenever the problem at hand is one that involves operations, processes, or quality control. The beauty of this 5 Whys analysis is that it manages to go to the roots of the issues; which are often masked in other methodologies. This technique is most often found in lean, Lean and Six Sigma methodologies as well as other Process Improvement and resolves all types of nonvalue-added situations.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
The RCA (Root Cause Analysis) Method called Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is used primarily to act before a problem occurs causing certain issues. It focuses specifically on understanding any process, system, or product and providing the defects which could arise due to the processes and define their effect. This is why any business would deploy the FMEA system to help minimize risk, determine severity levels and ensure control measures are placed to avert any failure incidents. This particular RCA method is mainly used in industries such as health care, the automotive sector and the aerospace industry where safety and regulation are of utmost importance.
Pareto Chart Analysis
A Pareto Chart draws upon the principle of the most frequent cause underpinning 80% of the problems which inelastic causes enable less than 20% of all problems. An RCA is quite effective in identifying the factors affecting a team’s performance by displaying critical and the worthiest data in the form of bars. Businesses embrace RCA-oriented methods of problems such as Quality issues resolution, enhancements in customer care, minimizing the firm’s operational inefficiencies and, most of all, Pareto application to the full range of ever since. This RCA frees the enterprise from having to correct all the defects since many defects involve correcting them in myriads of cases, and with that, it can only risk the best action for correcting the frequent defects.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Fault Tree Analysis, also referred to as FTA, constitutes a methodical as well as deductive method used for carrying out analysis of causes of failure in a system. This approach essentially maps the events leading to potential complications in a tiered format that helps the team identify the vulnerabilities within the system. It is typically practiced in fields such as Engineering, Information Technology, and Safety Management to boost the reliability of systems and avert the occurrence of malfunctions in the future. Notably, FTA finds extensive application in sectors where any equipment breakdowns and system malfunctions would translate into considerable economic and functional losses.
The key to enhancing business processes, minimizing defects, and improving results is through getting to the root of a dilemma. Any organization that uses the various RCA methodologies, understands them, and implements them properly will be able to solve problems, remove persistent issues and create a culture of improvement.


Common Pitfalls in Using RCA Templates and How to Avoid Them
Overcomplicating the Analysis Process
Overcomplicating the root cause analysis templates is one of the most common reasons why an organization will fail to utilize them. The mistake is caused by a breakdown in the process; teams do not steamroll unnecessary details, and irrelevant data and factors are brought in, complicating rather than simplifying things. RCA should be properly executed in identifying the root cause of an issue without unnecessary baggage. In order to achieve this, organizations should employ a properly structured RCA template which walks the users step by step ensuring all and only the necessary information is contained. Without losing sight of all the main factors contributing to the problem acceptable solutions can be based on such analysis.
Failing to Involve Key Stakeholders
Nothing is as serious as performing a root cause analysis with the exclusion of all those who are in direct touch with or affected by the problem. Typically, the misleading way in which RCA is done is that management or those in charge of quality assurance perform all the analysis work from an office and the rest of the employees on the ground are completely ignored or not consulted. Because of this, the resulting outcome might be either incomplete or even skewed. To do away with this, the RCA templates should be used in a cross-sectional manner within the organization. Employees from all corners should be involved in this as it helps them to gauge the situation and understand even more the problem that must be solved.
Neglecting Follow-Up on Implemented Solutions
One fails to see the accompaniment of RCA templates with the routines of corrective actions after implementation. This includes completing an analysis and presenting solutions only for the team to fail to track, measure, or evaluate the previously taken corrective action. Due to the lack of follow-up, there may be a recurrence or entirely new issues caused by the same problem. If this is to be headed off, the mitigation of issues via RCA methodologies should be extended to the application of continuous improvement practices. Holding consistent review meetings, selection of key parameters worth measuring, and accompanying implementation of the changes with the concern of who will be responsible for which part of it help facilitate and further promote resolution of the same problem over and over again.
Relying Solely on One RCA Methodology
Some businesses err on the side of caution and employ one root cause analysis technique for every problem. This sometimes is wrong because even though 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagrams, and Pareto diagrams are quite effective, some problems do not call for all of them. Too much reliance on a single approach may restrict analysis and result in premature conclusions. Rather, the sensible application of RCA templates relative to the problem and its attendant requirements is encouraged. Multiple techniques should be used, however, to confirm the results, especially in cases where one technique is inadequate.
Understanding the certain mistakes commonly made and taking the relevant actions enables the organization to exploit the full potential of RCA templates. Effectively carrying out the RCA method results in enhanced problem-solving skills, better operations, and the overall success of the business in the long run.
